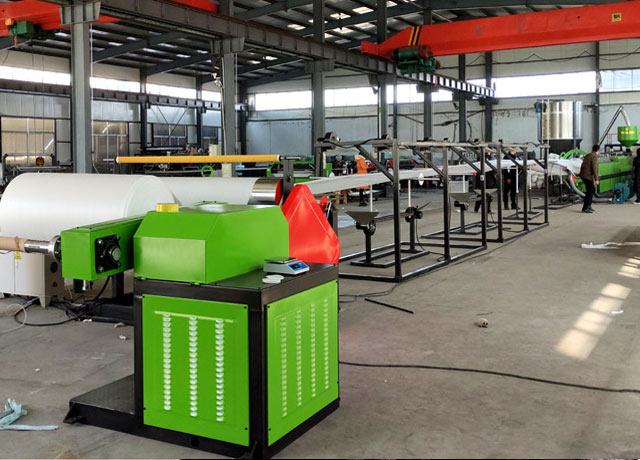
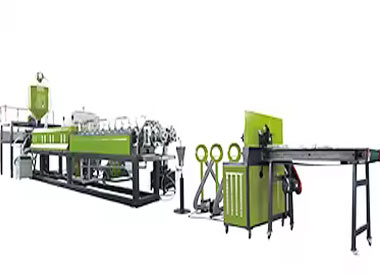
How does an EPE foam machine work?
EPE foam machine, also known as the “Physical Foaming LDPE Extrusion Unit.” Its core principle involves injecting liquid foaming agents (butane) and monoglyceride GMS into molten plastic under high temperature and pressure. As the melt exits the die, pressure rapidly drops, causing dissolved foaming agents to vaporize and expand instantly. This creates countless independent, sealed micro-bubbles, resulting in foamed material.
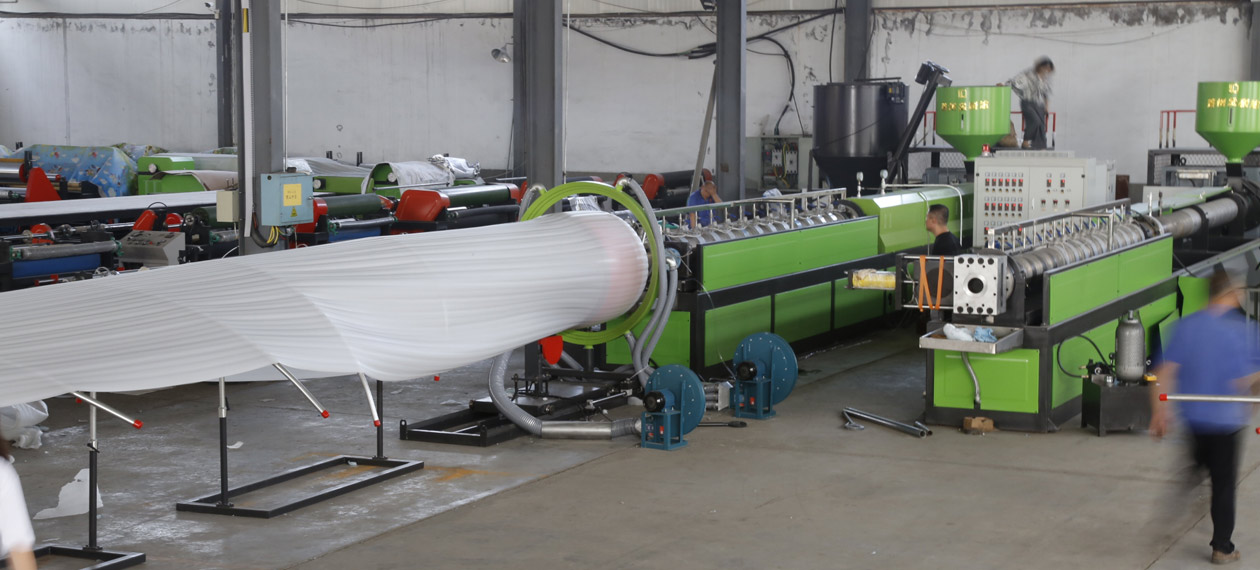

The entire EPE foam sheet production process can be divided into five key stages:
Stage 1: Plasticization and Melting
Raw Materials: Primarily low-density polyethylene (LDPE) pellets, supplemented with small amounts of talcum powder (nucleating agent, providing nucleation sites for bubble formation) and additives like monoglyceride.
Process: Raw materials are drawn into the hopper via an automatic feeder and enter the extruder barrel.
Function: The barrel is equipped with external electric heating coils and an internal rotating screw. Through heat conduction and friction, the screw gradually melts the solid plastic pellets into a viscous, uniform melt. Simultaneously, the screw compresses the melt to establish initial pressure.
Stage Two: High-Pressure Injection and Mixing
Key Action: This is the core of physical foaming. When the plastic melt reaches a specific temperature and pressure (typically exceeding butane's critical point), a liquid foaming agent (usually butane, or CO₂ in eco-friendly equipment) is precisely injected into the melt stream via a high-pressure metering pump.
State: The barrel maintains extremely high pressure and strictly controlled temperature. Under these conditions, the injected liquid butane does not vaporize immediately but is forcibly dissolved and diffused into the plastic melt, forming a homogeneous, high-pressure, high-temperature plastic-blowing agent fluid. The butane exists in a “supercritical” or forced dissolution state.
Stage Three: Cooling and Homogenization
Purpose: To achieve a fine, uniform cell structure, the melt must pass through a cooling section before exiting the die.
Process: The melt mixed with the foaming agent enters a mixing section equipped with water spray cooling. Here, the melt is precisely cooled. The cooling purpose is to increase melt viscosity, enabling sufficient strength to encapsulate gas during subsequent foaming. This prevents bubble coalescence or collapse, forming independent, uniform microcells.
Stage Four: Pressure Release Foaming
Critical Moment: The fully cooled and homogenized high-pressure melt is extruded through a ring die (for sheet production) or other specialized die heads.
Principle: The melt experiences immense pressure within the die. Upon extrusion through the narrow die gap, pressure instantly drops from dozens of atmospheres to atmospheric pressure. According to Henry's Law, gas solubility in liquid decreases with reduced pressure. This sudden pressure drop causes the butane dissolved in the melt to become supersaturated, instantly vaporizing into countless bubble nuclei that rapidly expand.
Result: The melt rapidly expands like “popcorn” at the outlet, constrained by the die shape to form a foamed blank of specified thickness and width.
Stage Five: Setting and Post-Processing
Tensioning and Flattening: The freshly foamed blank is hot and soft. It is drawn out at a constant speed via tensioning rollers and flattened by flattening rollers to prevent shrinkage and deformation.
Cooling and Setting: The foamed sheet passes through cooling rollers or air ducts to further reduce its internal temperature. This solidifies the cell structure, achieving stable dimensions and properties.
Winding and Cutting: Finally, the set EPE foam sheet is wound into large rolls by a winder or cut to specific widths as required, producing rolls or sheets.
The technical excellence of an EPE foam machine hinges on the precise, coordinated control of five critical parameters: temperature, pressure, rotational speed, butane injection volume, and cooling accuracy. This directly determines the final product's density uniformity, cell fineness, mechanical strength, and the stability and safety of the production process.
We hope this detailed explanation of the operating principles helps you better understand EPE foam machines.

Why Choose Us
China manufacturer of EPE foam machinery since 2003.EPE foam machine not only have covered all over China, but also have exported to more than 70 countries
Would you like to take a closer look at our offer?

You May Like:
We are making How does an EPE foam machine work? factory, manufacturer & supplier & exporter.We specialize in making EPE foam machine for over 20+ years