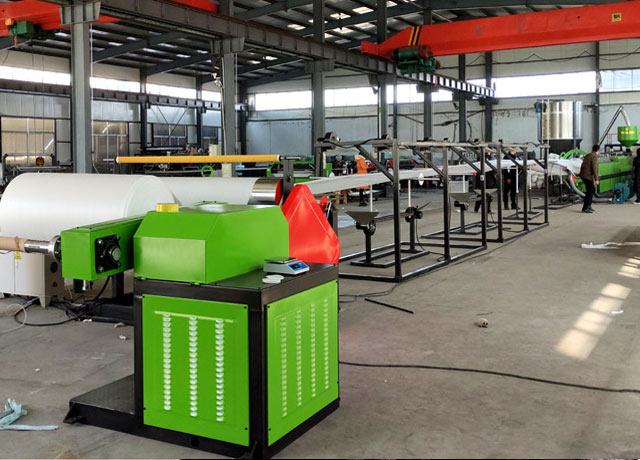
How to adjust the foaming density of an EPE foam machine? What are the minimum and maximum densities
This is a critical technical issue for evaluating the performance and process capabilities of an EPE foam machine. As a professional manufacturer of EPE foam machines, here is a detailed explanation for your reference:
Core Answer Summary
The density adjustment of EPE foam sheets is influenced by multiple factors: the main screw of the EPE foam machine, the extruder die head, the mold, the ratio of polyethylene raw material to additives like talcum powder, monoglyceride, and butane gas, as well as the temperature distribution across different zones of the foaming machine. It is a multi-variable coordinated control process. Standard machine models typically produce foams within a conventional density range of 16–35 kg/m³. Through specialized design and process optimization, the minimum achievable density can reach 12–15 kg/m³ (or lower), while the maximum achievable density can extend to 40–70 kg/m³ or higher. This depends on the equipment's capabilities and the compatibility of raw materials and processes.
I. Core Principles and Four Key Control Factors of Density Adjustment
Adjusting density fundamentally involves controlling the “ratio of plastic matrix to air bubbles per unit volume.” This is primarily achieved through the following four key factors:
| Controlling factors | Adjustment Method | Effects on Density (Principles) | Key Operating Points and Restrictions |
|---|---|---|---|
1. Foaming agent injection volume | Adjust the injection frequency or stroke of the high-pressure metering pump for butane (or CO₂). | The most fundamental and responsive method. Increasing injection volume → Reduced density (more and larger bubbles). Decreasing injection volume → Increased density. | Must be matched with temperature and pressure. Over-injection may cause cell coalescence, rupture, product shrinkage, or deformation; under-injection results in insufficient foaming. |
2. Extruder Melt Pressure and Temperature | Adjust the temperature of each heating zone and the screw speed of the extruder. | Fundamental Control. Increasing temperature/reducing viscosity → Facilitates bubble expansion → Reduces density. However, excessively high temperatures cause gas escape and bubble collapse. Maintaining stable high pressure is crucial for uniform gas dissolution. | An optimal process window is required. The temperature must be coordinated with the cooling section temperature to form an ideal “high-low-high” temperature gradient. |
3. Temperature Control in the Cooling Section of the Spray Zone | Adjust the temperature of the cooling section of the foaming machine. | Key precision control. Enhanced cooling → Increased melt viscosity → Suppression of excessive bubble expansion → Increased density. Reduced cooling → Lower viscosity → Full bubble growth → Decreased density. | Uneven cooling leads to non-uniform density profiles. This is the core technology for achieving low density while preventing bubble rupture. |
4. Nucleating Agent and Raw Materials | Adjust the addition ratio of talc powder (nucleating agent) or modify the LDPE/recycled material ratio. | Structural Adjustment. Increasing nucleating agent → More bubble nuclei → Finer cell structure → Enables lower density with uniform cell distribution. Using high melt flow index raw materials facilitates easier foaming. | The melt index (MI) and purity of raw materials influence foaming behavior. A high proportion of recycled material typically leads to increased density and a narrower density range. |
II. What are the minimum/maximum densities achievable for EPE foam? — Technical Limit Analysis
Density Type | Typical Range (kg/m³) | Implementation Conditions and Technical Challenges | Product Features and Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
Standard Scope of Work | 18 - 35 | Standard equipment, utilizing conventional virgin LDPE resin, offers a wide process window, the most stable production, and the highest cost-effectiveness. | Balanced performance, suitable for over 90% of packaging cushioning and general protective materials. |
Extreme low-density range | 12 - 18 | Technical Challenges: Requires extremely high gas retention capacity and bubble stability. Requirements for Implementation: 1. Specialized screw: Exceptionally strong mixing and dissolving capability. 2. Precision temperature control and cooling. 3. Premium raw materials: High melt flow index virgin resin combined with high-efficiency nucleating agents. 4. High-precision foaming agent metering system. | Extremely soft with excellent cushioning properties, but with reduced compressive strength and surface hardness. Used for ultra-lightweight packaging and fillers. |
Extreme High-Density Range | 40 - 70+ | Technical Challenges: Requires suppression of foaming while maintaining high melt strength. Requirements for Implementation: 1. Significantly reduce foaming agents, approaching near-zero foaming. 2. Enhance cooling to achieve rapid solidification. 3. Allow for increased filler content (e.g., calcium carbonate). | High hardness, impact resistance, and excellent mechanical strength, comparable to EVA or foam plastic sheets. Used for heavy-duty packaging, structural padding, and floor mat substrates. |
Important Notice:
The Cost of Pushing Limits: Production at extreme densities involves a very narrow process window, high sensitivity to equipment parameter fluctuations, potential increases in scrap rates, and physical properties skewed toward one end of the spectrum (e.g., lower densities become softer, higher densities become harder).
Safety Warning: When pursuing excessively low densities, excessive butane injection or improper processing can easily lead to excessive butane residue in the product. This results in an odor during storage, flammability, and abnormally soft EPE foam hardness—potentially causing post-shrinkage and failing to achieve the intended protective effect.
Summary:
Density adjustment for EPE foam is the core function of our equipment. Our EPE foam machine operates comfortably within a range of 14-35 kg/m³, where adjustments are highly responsive and stable. Through process optimization, we can achieve a minimum density of approximately 13 kg/m³ or even 12 kg/m³ (ultra-light and soft), and a maximum exceeding 50 kg/m³ (high hardness). The specific achievable limits depend on raw material quality and long-term production stability requirements. We recommend first defining your core product specifications, then conducting targeted sampling to identify the density process point offering the best cost-performance ratio.

Why Choose Us
China manufacturer of EPE foam machinery since 2003.EPE foam machine not only have covered all over China, but also have exported to more than 70 countries
Would you like to take a closer look at our offer?

You May Like:
We are making How to adjust the foaming density of an EPE foam machine? What are the minimum and maximum densities factory, manufacturer & supplier & exporter.We specialize in making EPE foam machine for over 20+ years