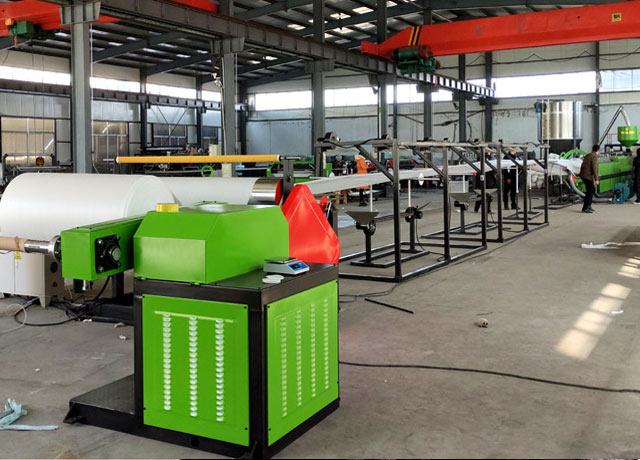
What is EPE Foam? A Comprehensive Analysis of EPE Foam's Exceptional Properties and Core Advantages
I. EPE Foam: The Birth of a Revolutionary Packaging Material
EPE foam, scientifically known as Expanded Polyethylene (EPE), is a novel eco-friendly packaging material featuring a non-crosslinked closed-cell structure produced through physical foaming technology. Prolonged exposure to direct ultraviolet radiation causes degradation and decomposition. It is not a natural product but rather a testament to human ingenuity in materials science.
Origins and Development Timeline
- Key Milestones: EPE foam technology was first developed in Europe and the United States in the early 1990s.
- Introduction to China: Entered the Chinese market in the late 1990s, rapidly replacing traditional packaging materials.
- Technological Evolution: From initial simple foaming to today's precision-controlled foaming, with densities ranging from 14 kg/m³ to over 40 kg/m³ to meet diverse requirements
II. Core Manufacturing Process of EPE Foam: The Technical Secrets of Physical Foaming
1. Basic Raw Materials for EPE Foam
- Primary Components: Low-density polyethylene (LDPE) serves as the main substrate, accounting for approximately 95%
- Foaming Agents: Butane or carbon dioxide as physical foaming agents, free of ozone-depleting substances like CFCs
- Auxiliary Materials: Small amounts of talc (nucleating agent), monoglyceride (lubricant), and color masterbatch
2. Detailed EPE Foaming Process
```
Raw material mixing → Heating and melting → Injection of foaming agent → Uniform mixing → Extrusion molding → Cooling and setting → Winding/slitting
```
EPE Foam Technical Essentials:
- Temperature Control: Melting temperature strictly maintained between 115-130°C
- Pressure Management: Injection pressure of foaming agent kept stable to ensure uniform bubble distribution
- Cooling Rate: Directly impacts final density and hardness of EPE foam
3. Critical Significance of Closed-Cell Structure
Each independent bubble measures approximately 0.5-3 mm in diameter, with bubble walls composed of polyethylene film. Bubbles remain non-interconnected. This structure defines EPE foam's three fundamental properties:
- Moisture resistance: Water cannot permeate within the material
- Stable cushioning performance: Each bubble functions as an independent elastic unit
- Thermal insulation: Stagnant air serves as the optimal thermal insulating medium
III. Eight Key Physical Properties of EPE Foam: Data-Driven Performance Analysis
1. EPE Foam Density and Weight Ratio
- Density Range: 14–40 kg/m³ (adjustable as needed)
- Weight Advantage: Weighs only 1/3 to 1/5 of traditional packaging materials for the same volume
- Practical Impact: Significantly reduces transportation costs and enhances logistics efficiency
2. EPE Foam Cushioning and Impact Resistance
- Energy Absorption Rate: Absorbs 70%-85% of impact energy
- Permanent Deformation Rate: <5% (National Standard requirement), premium products achieve <2%
- Test Standard: Passes ASTM D1596 drop test—100 drops from 1-meter height with no noticeable deformation
3. EPE Foam Flexibility and Formability
- Flexibility: Can bend 180° without fracture
- Forming Methods: Supports stamping, cutting, heat sealing, lamination, and other processing techniques
- Design Freedom: Enables complex custom packaging that perfectly conforms to product contours
4. EPE Foam Temperature Stability
- Operating Temperature Range: Maintains stable performance from -40°C to +80°C
- Low-Temperature Testing: >95% rebound rate after 24 hours at -40°C
- High-Temperature Testing: No stickiness or deformation at +80°C
5. Moisture Resistance and Chemical Resistance
- Water Absorption Rate: <0.01g/cm² (24-hour immersion)
- Chemical Resistance: Resists most acids, alkalis, and salt solutions; not resistant to strong oxidizing acids
- Practical Application: Suitable for high-humidity environments like maritime shipping
6. Thermal Insulation Performance
- Thermal Conductivity: 0.038–0.042 W/(m·K)
- Insulation Comparison: Equivalent to 80% of traditional insulation materials' thermal performance
- Energy Savings: Reduces cold loss by over 30% in cold chain packaging
7. Flame Retardancy Rating
- Standard Classification: Standard grade, flame-retardant grade (self-extinguishing when removed from flame)
- Test Method: Passes UL94 HF-1 rating
- Applications: Electronics, automotive interiors, and other flame-retardant-required fields
8. Environmental & Safety Properties
- Chemical inertness: Emits no toxic gases, contains no heavy metals
- Food contact safety: Complies with FDA 21 CFR 177.1520 standards
- Recyclability: 100% recyclable and reusable
IV. Performance Comparison Between EPE Foam and Traditional Packaging Materials
Feature Comparison | EPE foam | EPS(Expanded Polystyrene) | EPP(Expanded polypropylene) | Bubble wrap | Corrugated cardboard |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Buffering performance | ★★★★★ | ★★★☆☆ | ★★★★★ | ★★☆☆☆ | ★★☆☆☆ |
Weight density | ★★★★★ | ★★★☆☆ | ★★★★☆ | ★★★☆☆ | ★★☆☆☆ |
Moisture-proof and waterproof | ★★★★★ | ★★☆☆☆ | ★★★★☆ | ★★★★★ | ★☆☆☆☆ |
Environmental Rating | ★★★★☆ | ★☆☆☆☆ | ★★★★★ | ★★☆☆☆ | ★★★★★ |
Processing difficulty | ★★★☆☆ | ★★★★★ | ★★★★☆ | ★★☆☆☆ | ★★☆☆☆ |
Total Cost | ★★★★☆ | ★★★☆☆ | ★★☆☆☆ | ★★★☆☆ | ★★★★★ |
Data Analysis: EPE foam achieves optimal balance across multiple key metrics, excelling particularly in cushioning, moisture resistance, and overall cost-effectiveness.
V. Detailed Applications of EPE Foam in Five Core Sectors
1. Electronics Packaging Sector
- Laptops: Corner bumpers, keyboard protective layers, full-coverage cushioning
- LCD screens: Edge protection, surface isolation shielding
- Precision instruments: Anti-static EPE foam (surface resistance 10⁶-10⁹Ω)
- Key advantages: Scratch prevention, static dissipation, and thorough cushioning
2. Medical Devices and Precision Instruments
- CT/MRI components: Customized irregular-shaped packaging
- Surgical instruments: Individually compartmentalized packaging for direct sterile transfer to operating rooms
- Glassware: Multi-angle shockproof design
- Special requirements: Some applications require anti-static and sterile processing
3. Automotive Parts Packaging
- Headlight assemblies: 3D packaging to prevent transport abrasion
- Dashboards: Surface protection against scratches
- Engine components: Heavy-duty EPE foam (density 25-30 kg/m³)
- Development trends: Co-development with OEMs, modular packaging design
4. Furniture and Home Goods
- Glass furniture: Reinforced edge protection
- Ceramic sanitaryware: Full-coverage wrapping with multi-layer cushioning
- Wooden furniture: Corner protection against impact damage
- Innovative application: EPE foam laminated with PE film for enhanced tear resistance
5. Cold Chain Logistics & Fresh Produce Delivery
- Pharmaceutical cold chain: Vaccine transport at 2-8°C with 48-72 hour insulation duration
- Fresh food e-commerce: Specialized packaging for fruits and seafood to prevent crushing and spoilage
- Insulation design: Multi-layer composite structure (EPE foam + aluminum foil + PE film)
- Economic benefits: Over 35% cost reduction compared to traditional cold chain packaging
VI. Four Major Processing Directions for EPE Foam
1. Cutting and Forming
- Equipment Requirements: EPE foam vertical cutter, horizontal cutter
- Precision Control: ±0.5mm (±0.2mm for precision cutting)
- Production Efficiency: Manual cutting: 300-500 pieces/hour; Automatic cutting: up to 2000 pieces/hour
2. Heat Sealing and Laminating
- Bonding Methods: Flame bonding, hot air bonding, hot plate bonding
- Composite Materials: PE film, woven fabric, aluminum foil, non-woven fabric, etc.
- Strength Testing: Peel strength up to 3-5N/25mm
3. Stamping
- Die Types: Knife dies, metal dies
- Processing Depth: Maximum single-stroke thickness up to 100mm
- Dimensional Accuracy: ±0.3mm
4. Special Treatments
- Anti-static Treatment: Surface resistance controllable between 10⁶-10⁸Ω
- Antibacterial Treatment: Incorporation of antimicrobial agents like silver ions
- Printing Identification: Screen printing, inkjet coding
VII. EPE Foam's Dual Advantages in Environmental Protection and Sustainable Development
1. Environmental Friendliness in Production
- Energy Consumption: Over 40% more energy-efficient than EPS production
- Exhaust Emissions: Only water vapor and minimal carbon dioxide, no toxic gases
- Water Resource Usage: Closed-loop water circulation system with zero wastewater discharge
2. Post-Use Recycling and Processing
- Physical Recycling: Shredding → Pelletizing → Reprocessing, recyclable 5-7 times
- Chemical Recycling: High-temperature pyrolysis into fuel oil and gas
- Biodegradation: New biodegradable EPE foam under development, naturally degrades in 6-12 months
3. Full Life Cycle Carbon Footprint Analysis
- Compared to traditional EPS: Over 60% reduction in carbon emissions
- Compared to paper products: 50% lower production energy consumption, 90% reduced water usage
- Comprehensive assessment: EPE foam ranks among the lowest-carbon plastic packaging materials available
VIII. Technological Trends in the EPE Foam Industry
1. Material Innovation Directions
- High-elasticity EPE foam: Rebound rate >95%, used for precision instruments
- Ultra-low-density EPE foam: Density <15kg/m³, used for ultra-lightweight packaging
- Multifunctional composites: EPE foam combined with phase change materials for smart temperature-controlled packaging
2. Process Technology Upgrades
- In-line composite technology: Single-step molding of multi-layer composite materials
- Digital molding: 3D scanning + automated cutting for personalized customization
- Smart production: IoT + big data for optimized production parameters
3. Application Expansion
- Building insulation: Replacing traditional insulation materials
- Sports protection: Athletic equipment and protective gear
- Agricultural applications: Seedling mats and thermal cover materials
IX. Core Recommendations for Potential EPE Foam Machine Manufacturers
1. Entry-Level Options
- Initial Investment: RMB 150,000–300,000 to launch small-scale processing operations
- Equipment Configuration: Basic setup of foaming machine + cutting machine + heat sealing machine
- Market Positioning: Serve local SMEs by specializing in niche markets
2. Key Technical Control Points
- Density Control: Maintain stability within ±1 kg/m³
- Bubble Uniformity: Visually inspect cross-sections for even bubble distribution
- Edge Integrity: Cutting edges free of fraying or deformation
3. Quality Control System
- Incoming Inspection: LDPE melt flow index testing (MFI: 2-4g/10min)
- Process Control: Density and thickness checks every 2 hours
- Finished Product Testing: Drop tests, compression tests, environmental tests
X. Conclusion: Why is EPE foam the inevitable choice for the packaging industry?
EPE foam is not a perfect material, but it currently offers the most balanced packaging solution. It perfectly resolves three core contradictions in the packaging industry:
1. The contradiction between protection and cost: It provides superior protective performance at 20%-30% lower cost than traditional materials.
2. The conflict between functionality and environmental sustainability: It maintains 100% recyclability while delivering multiple functionalities.
3. The conflict between standardization and customization: Through flexible processing techniques, it produces fully customized packaging products from standardized raw materials.
For those preparing to enter this industry, EPE foam represents more than just a material—it embodies a technology-driven, environmentally conscious business opportunity with vast market potential. Its moderate technical barriers, sustained market growth, and expanding applications make it an ideal entry point for small and medium-sized manufacturers.
The data speaks for itself: The global EPE foam market maintains an annual growth rate of 6%-8%, with China's market surging at 10%-12%. Driven by three key engines—e-commerce packaging, precision instruments, and cold chain logistics—this growth is projected to accelerate rather than decelerate over the next five years.
Choosing EPE foam means entering an industry track with both immediate market demand and long-term growth potential. As manufacturers of EPE foam extruders, we offer more than just equipment—we provide a complete solution encompassing technical training, process optimization, and market integration.
Extended Reflection: As you delve into each characteristic of EPE foam, you see more than just material specifications. You witness the potential for enhanced protection across countless products, the economic benefits of reduced shipping losses, and the social responsibility of contributing to environmental sustainability. This is why EPE foam is evolving from a common packaging material into an indispensable foundation for modern manufacturing.

Why Choose Us
China manufacturer of EPE foam machinery since 2003.EPE foam machine not only have covered all over China, but also have exported to more than 70 countries
Would you like to take a closer look at our offer?

You May Like:
We are making What is EPE Foam? A Comprehensive Analysis of EPE Foam's Exceptional Properties and Core Advantages factory, manufacturer & supplier & exporter.We specialize in making EPE foam machine for over 20+ years